Approximately 45,000 Jenkins servers are still vulnerable to CVE-2024-23897, a critical remote code execution (RCE) flaw, despite the release of a patch addressing the issue last week. Making matters worse, researchers have discovered the public availability of multiple public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits.
Jenkins is a popular open-source automation server for continuous integration and continuous delivery/deployment (CI/CD) that provides developers with an environment to build, test, and deploy software.
CVE-2024-23897 is an issue in Jenkins’ command-line interface (CLI) that allows attackers to read arbitrary files on the Jenkins controller's file system. Depending on permissions and the server’s configuration, successful exploitation can lead to remote code execution and the access/manipulation of sensitive data.
According to recent data from the Shadowserver Foundation, nearly 45,000 Jenkins servers remain vulnerable to CVE-2024-23897. Nearly half of those servers are located in the U.S. and China.
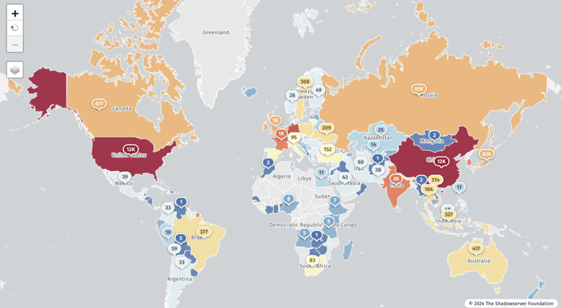
Deployment of Jenkins servers worldwide (Source: Shadowserver Foundation)
Source: Bleeping Computer
Analysis
The large footprint of the vulnerable Jenkins servers and the availability of multiple proof-of-concept exploits represent a significant cybersecurity threat to both Jenkins users and third parties.
This is because a successful compromise could have future impacts, such as developing exploits for deployed software. Since threat actors may have access to source code, the insertion of malicious code into projects in development could result in a supply chain attack once the software is deployed.
It’s imperative that users of Jenkins servers install the latest security patch and investigate for signs of compromise as soon as possible.
Mitigation
Field Effect’s elite team of Security Intelligence professionals constantly monitor the cyber threat landscape for vulnerabilities discovered in software, appliances and operating systems. This research contributes to the timely deployment of signatures into Covalence to detect and mitigate the exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Covalence users are automatically notified when vulnerable software is detected in their environment and are encouraged to review these AROs as quickly as possible via the Covalence portal.
Field Effect strongly encourages users of affected Jenkins servers to install the latest security patch as soon as possible per the Jenkins security bulletin. Users unable to do so should disable access to the CLI.
Related articles
