Cybersecurity researchers have released proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for a critical vulnerability in Fortinet’s Enterprise Management Software (EMS) that is now being exploited in the wild.
The vulnerability, originally discovered and reported by the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) and designated CVE-2023-48788, is an SQL injection in the DB2 Administration Server (DAS).
The flaw affects EMS versions 7.0 and 7.2, and could allow unauthenticated threat actors to execute remote code with system-level privileges in low-complexity attacks that don't require user interaction.
Source: Bleeping Computer
Analysis
According to the Shadowserver Foundation, there are over 400 Fortinet EMS instances deployed worldwide, with the largest concentration (348) found in the US.
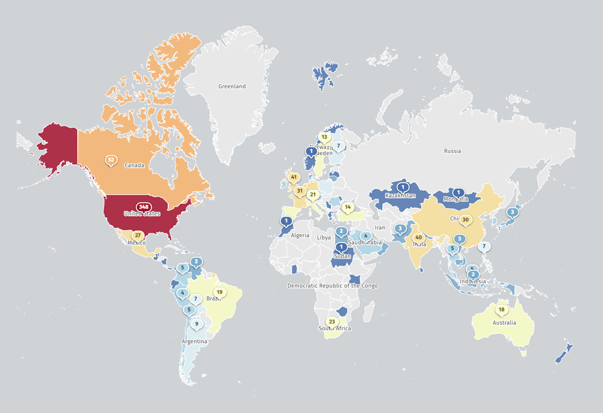
Image 1: Map of Fortinet EMS deployments (Source: Shadowserver Foundation)
Given the public availability of PoC exploit code and the critical nature of the vulnerability, it's fortunate that the footprint of potentially affected devices is relatively small compared to previous vulnerabilities found in Fortinet products.
For example, CVE-2024-21762, an out-of-bounds write vulnerability that could enable remote code execution impacted approximately 300,000 Fortinet FortiOS SSL VPN instances deployed worldwide.
Mitigation
Field Effect’s elite team of Security Intelligence professionals constantly monitor the cyber threat landscape for vulnerabilities discovered in software, appliances and operating systems. This research contributes to the timely deployment of signatures into Covalence to detect and mitigate the exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Covalence users are automatically notified when vulnerable software is detected in their environment and are encouraged to review these AROs as quickly as possible via the Covalence portal.
Field Effect strongly encourages users of Fortinet EMS to update to a secure version as soon as possible and investigate for any sign of compromise.
Related articles
