The Google Cloud Vulnerability Research team has discovered six vulnerabilities in Rsync, a popular file synchronization tool for Unix systems.
The most severe vulnerability, designated CVE-2024-12084 and provided a critical CVSS rating of 9.8, is a heap buffer overflow flaw stemming from the improper handling of checksum data that leads to out-of-bounds writes in the buffer. Successful exploitation of the flaw could allow threat actors with anonymous read access to execute remote code on vulnerable Rsync servers.
The other vulnerabilities encompass issues including improper information disclosure, file leaks, path traversal, and symbolic-link race conditions.
Patches for the vulnerabilities have been released in Rsync version 3.4.0, and users are strongly advised to update to this version to mitigate potential risks. So far, no indication of active exploitation or that proof-of-concept exploit code has been made public.
Source: Bleeping Computer
Analysis
Vulnerabilities in file transfer and synchronization tools similar to Rsync, such as MOVEit, Accellion FTA, GoAnywhere MFT, SolarWinds Serv-U, and FileZilla, have been exploited by attackers to steal sensitive data or deploy ransomware. Tools like Rsync are widely used in corporate environments, making them high-value targets. Exploiting misconfigurations, unpatched systems, and exposed services grants attackers unauthorized access, often leading to data breaches, extortion, and advanced attacks. Regular patching, access restrictions, and security monitoring are essential to mitigate these risks and prevent similar exploits.
According to a Shodan search, approximately 660,000 Rsync servers are deployed worldwide, with the vast majority (523,000) in China.
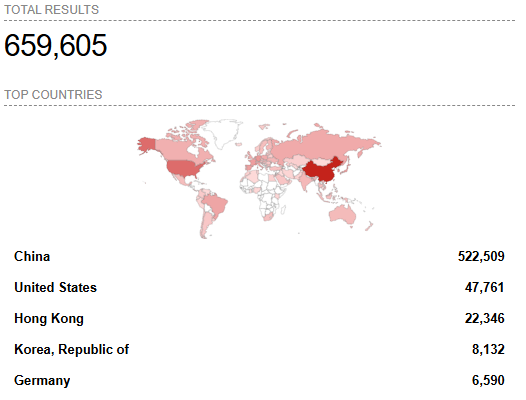
Image 1: Results of search for Rsync servers (Source: Shodan.io)
It's unclear if all 660,000 internet-connected Rsync servers are impacted by the newly discovered vulnerabilities. However, there still likely exists a large attack surface for threat actors to target. It’s likely only a matter of time before threat actors develop the exploit code required to seize this threat opportunity, thus organizations running vulnerable versions of Rsync must patch them as soon as possible.
Mitigation
Field Effect’s elite team of Security Intelligence professionals constantly monitor the cyber threat landscape for vulnerabilities discovered in file-sharing software like Rsync. This research contributes to the timely deployment of signatures into Field Effect MDR to detect and mitigate the exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Field Effect MDR users are automatically notified if a vulnerable version of a file synchronization tool is detected in their environment and are encouraged to review these AROs as quickly as possible via the Field Effect Portal.
Field Effect strongly encourages users of the affected Rsync versions to update to the latest version as soon as possible, in accordance with Openwall’s advisory.
Related Articles
