Palo Alto Networks (PAN) has confirmed that it has observed threat activity exploiting an unauthenticated remote command execution (RCE) vulnerability against a limited number of internet-exposed management interfaces in its firewalls. The vulnerability, which is yet to receive a CVE designation, has been provided a critical CVSS score of 9.3.
Earlier this week, PAN advised that its investigation into claims of a ‘potential’ RCE vulnerability in the PAN-OS management interface hadn’t revealed any signs of active exploitation. Nonetheless, it recommended that users of the affected PAN firewalls ensure their PAN-OS management interface is properly configured to restrict Internet access to, and only allow connections from, trusted internal IP addresses.
In its latest update, PAN advised that it is preparing to release fixes and threat prevention signatures to patch the vulnerability. Securing access to the management interface remains the best method to protect impacted firewalls until the patch is available.
Source: The Hacker News
Analysis
The assignment of a critical 9.3 CVSS score to this vulnerability is likely due to fact that the vulnerability can be exploited by unauthenticated threat actors, thus increasing the risk the flaw poses. Exploitation of an RCE bug could allow threat actors to modify firewall rules, enabling unrestricted access to the target’s network.
Fortunately, it appears that impacted users are heeding PAN’s warning and are taking actions to make sure their PAN-OS management interfaces aren’t internet-exposed. According to the Shadowserver Foundation, on November 12 there were nearly 11,000 instances of PAN-OS management interfaces exposed to the internet that could potentially be vulnerable to PAN-SA-2024-0015, PAN’s internal reference number for the RCE.
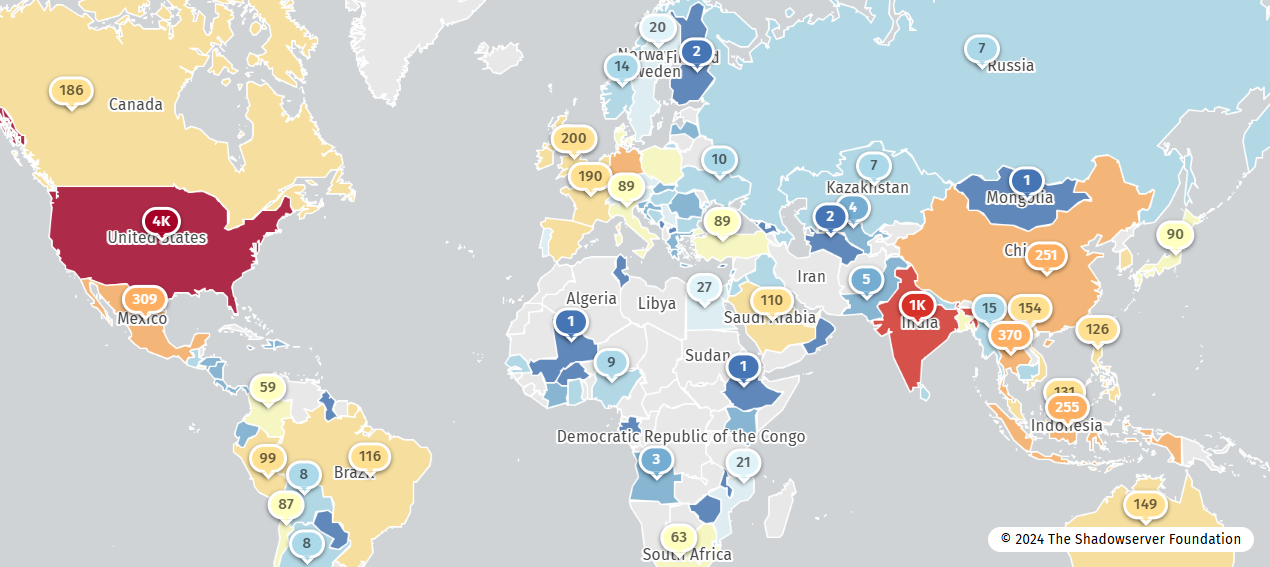
On November 15, it appears that the number of potentially exploitable exposed PAN-OS management interfaces has decreased to 6,000. Hopefully this trend continues until a patch is released by PAN.
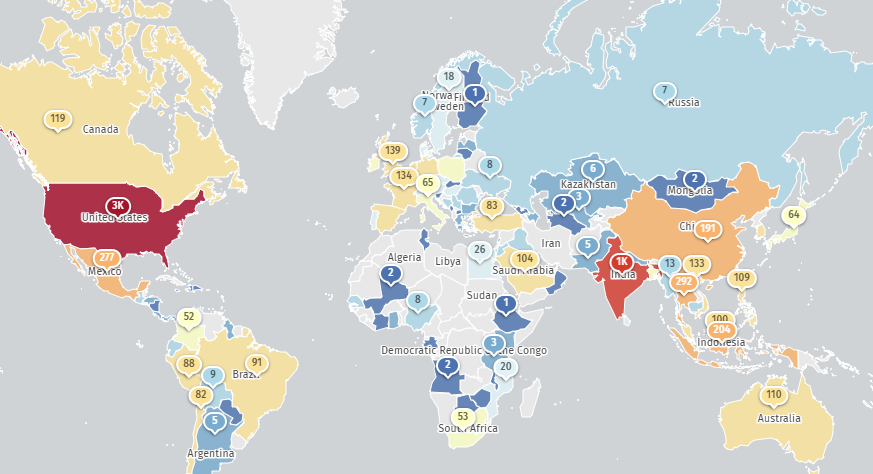
Mitigation
Field Effect’s elite team of Security Intelligence professionals constantly monitor the cyber threat landscape for vulnerabilities discovered in software, appliances, and operating systems. This research contributes to the timely deployment of signatures into Field Effect MDR to detect and mitigate the exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Field Effect MDR users are automatically notified when vulnerable software is detected in their environment and are encouraged to review these AROs as quickly as possible via the Field Effect MDR portal.
Field Effect strongly encourages users of potentially vulnerable Palo Alto firewalls to ensure the management interface is configured properly by following the guidance in Palo Alto’s advisory.
Related Articles
